
A tool for interpreting simplified-model results from the LHC
Mohammad Mahdi Altakach, Sabine Kraml, Andre Lessa, Sahana Narasimha, Timothée Pascal, Humberto Reyes-González, Théo Reymermier, Wolfgang Waltenberger
Previously involved in SModelS: Gaël Alguero, Federico Ambrogi, Jan Heisig, Charanjit K. Khosa, Juhi Dutta, Suchita Kulkarni, Ursula Laa, Veronika Magerl, Wolfgang Magerl, Philipp Neuhuber, Doris Proschofsky, Camila Ramos, Jory Sonneveld, Michael Traub, Yoxara Villamizar, Matthias Wolf, Alicia Wongel7 Aug 2025: SModelS version 3.1.0 available (what’s new)
- Introduced minmassgapISR parameter for controlling the mass compression for ISR topologies. WARNING: with the default setting, behavior for ISR topologies differs from previous versions!
- Improved the syntax of pyhf fields in globalInfo.txt:jsonFiles
- Small fixes in analyses combinations, better handling exceptions in likelihood computations, we thank Leo Constantin for help with a bug fix concerning failed likelihood computations
- Fixed an inconsistency with the upper limits from analysis combinations. analysis-combined ULs may be different by up to ~ 10%
- Improved way of finding upper limits, UL computations may vary slightly numerically
- renamed ‘expected’ flag to an ‘evaluationType’ enum throughout the code
- Bumped up pythia8 from 8308 to 8315
- Bumped up lhapdf used in resummino from 6.5.4 to 6.5.5
- Database extension: ATLAS-EXOT-2018-06 (EM), additional topologies for CMS-EXO-20-004 (EM). WARNING: database shipped with 310 is currently at beta!
- Small fixes in database: ATLAS-SUSY-2018-14 (UL), ATLAS-SUSY-2018-31 (EM), CMS-SUS-20-004 (UL) – results for these analyses may vary with respect to the previous version!
20 Aug 2024: SModelS version 3.0.0 available (what’s new)
- Paper for version 3.0: arXiv:2409.12942
- New graph-based topology description now allows SModelS to handle arbitrary simplified model topologies, without the need of an imposed Z2 symmetry.
- Important database update with several non-Z2 signatures (resonances, monojet, RPV)
- A detailed documentation is available in the online manual
- For instructions on how to install SModelS, check the installation section in the manual.
- This tutorial is available from the latest Reinterpetation workshop.
- You may also want to check the release notes, the database releases and known issues
- Here are the list of analyses in the latest database version, the respective validation plots and an SMS dictionary explaining the Tx names used by SModelS.
- A discussion of re-interpretation methods and tools, and recommendations about the presentation of results can be found in this report by the LHC Reinterpretation Forum, arXiv:2003.07868.
- SModelS support for pyhf likelihoods is described in arXiv:2009.01809 and the main novelties of SModelS v2 in arXiv:2112.00769.
- An update of the micrOMEGAs interface for SModelS v2.2 is available on Zenodo
Mailing lists:
- For questions and comments, send an e-mail to: smodels-users@lists.oeaw.ac.at.
- To receive updates and announcements, subscribe to smodels-info.
If you use SModelS, please cite the following papers:
- SModelS v3: going beyond Z2 topologies, Mohammad Mahdi Altakach, Sabine Kraml, Andre Lessa, Sahana Narasimha, Timothée Pascal, Camila Ramos, Yoxara Villamizar, Wolfgang Waltenberger, arXiv:2409.12942 JHEP 11 (2024) 074
- SModelS v2.3: enabling global likelihood analyses, Mohammad Mahdi Altakach, Sabine Kraml, Andre Lessa, Sahana Narasimha, Timothée Pascal, Wolfgang Waltenberger, arXiv:2306.17676, SciPost Phys. 16 (2024) 101
- Constraining new physics with SModelS version 2, Gael Alguero, Jan Heisig, Charanjit Khosa, Sabine Kraml, Suchita Kulkarni, Andre Lessa, Humberto Reyes-Gonzalez, Wolfgang Waltenberger, Alicia Wongel, arXiv:2112.00769, JHEP 08 (2022) 068
- A SModelS interface for pyhf likelihoods, Gael Alguero, Sabine Kraml, Wolfgang Waltenberger, arXiv:2009.01809, CPC March 2021, 107909
- SModelS database update v1.2.3, Charanjit K. Khosa, Sabine Kraml, Andre Lessa, Philipp Neuhuber, Wolfgang Waltenberger, arXiv:2005.00555, LHEP 158 2020
- SModelS v1.2: long-lived particles, combination of signal regions, and other novelties, Federico Ambrogi et al., arXiv:1811.10624, CPC 251, June 2020, 106848
- Constraining new physics with searches for long-lived particles: Implementation into SModelS, Jan Heisig, Sabine Kraml, Andre Lessa, arXiv:1808.05229, Phys.Lett. B788 (2019) 87-95.
- SModelS extension with the CMS supersymmetry search results from Run 2, Juhi Dutta, Sabine Kraml, Andre Lessa, Wolfgang Waltenberger, arXiv:1803.02204, LHEP 1 (2018) no.1,5-12
- SModelS v1.1 user manual: improving simplified model constraints with efficiency maps, Federico Ambrogi, Sabine Kraml, Suchita Kulkarni, Ursula Laa, Andre Lessa, Veronika Magerl, Jory Sonneveld, Michael Traub, Wolfgang Waltenberger arXiv:1701.06586, CPC 227 (2018) 72-98
- SModelS: a tool for interpreting simplified-model results from the LHC and its application to supersymmetry, Sabine Kraml, Suchita Kulkarni, Ursula Laa, Andre Lessa, Wolfgang Magerl, Doris Proschofsky, Wolfgang Waltenberger, arXiv:1312.4175, EPJC (2014) 74:2868
Moreover
- If you use the cross section calculator please cite Pythia and NLLfast
- If you use the Fastlim results in the database, please cite Fastlim 1.0 arXiv:1402.40492v1, EPJC74 (2014) 11.
For convenience a references.bib file containing all relevant references is provided with the code. Likewise, a database.bib file with references to all the ATLAS and CMS analyses used is provided in the text database. ————————————————————————
Working principle
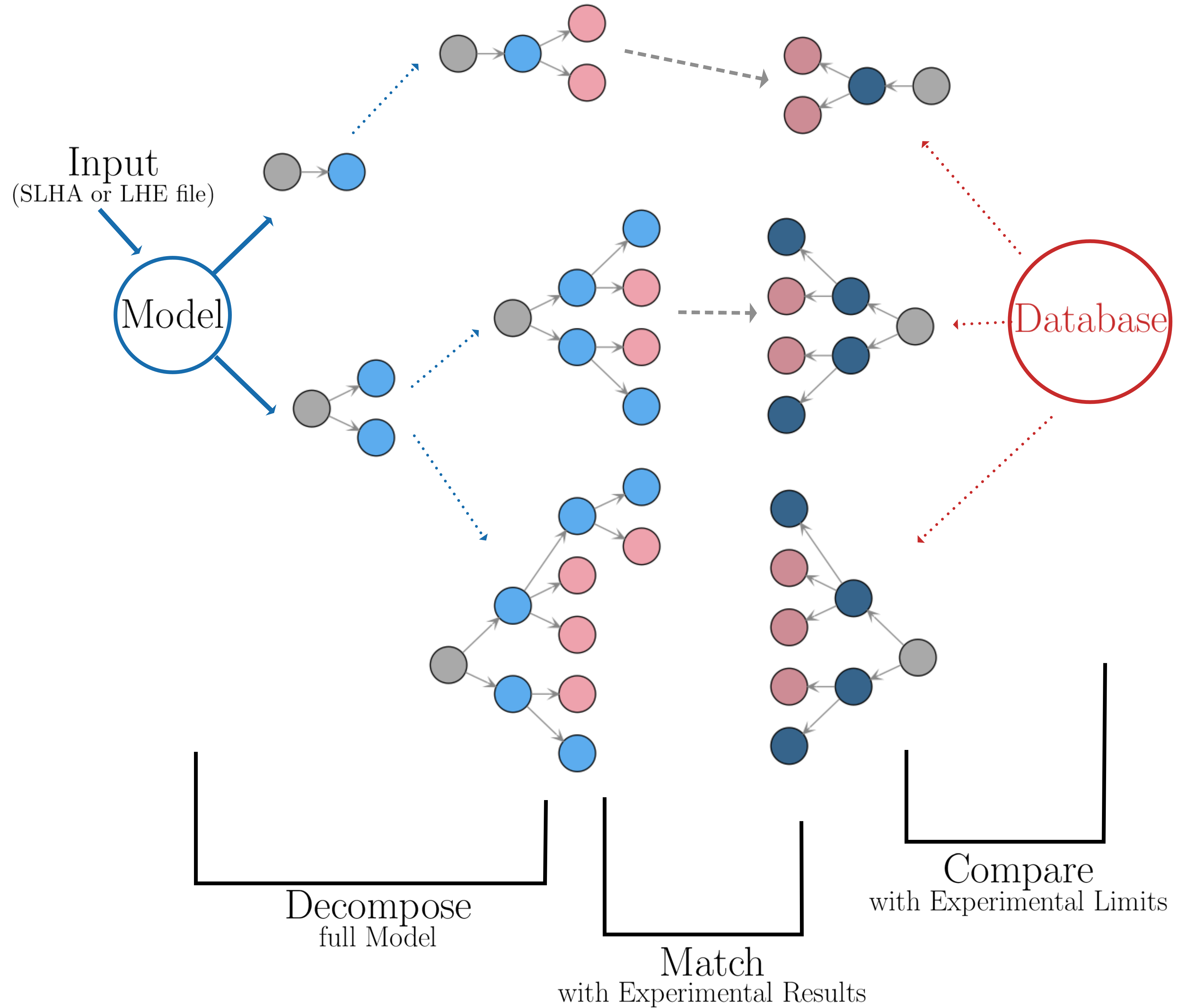
SModelS is an automatic, public tool for interpreting simplified-model results from the LHC. It is based on a general procedure to decompose Beyond the Standard Model (BSM) collider signatures into Simplified Model Spectrum (SMS) topologies. Our method provides a way to cast BSM predictions for the LHC in a model independent framework, which can be directly confronted with the relevant experimental constraints. The main SModelS ingredients are
- the decomposition of the BSM spectrum into SMS topologies
- a database of experimental SMS results
- matching between the decomposition and results database, including the tools to perform various kinds of statistical inference
as illustrated in the scheme below.
Code and Database updates
- For code and database releases, see Download
Experimental results in the database
- Here is the list of analyses contained in the latest database version
- Same as above but including superseded analyses
- Pretty validation plots for all analyses
- We also provide an SMS dictionary explaining the Tx names used by SModelS
Publications and Talks
See the publications and talks page





